
This Articles Contents
MySQL history
SQL stands for Structured Query Language but was initially conceptualized as SEQUEL Structured English Query Language. The name was changed from SEQUEL to SQL because another company already held the copyright to SEQUEL. SQL was originally developed by two IBM engineers to manipulate data stored in an IBM-developed database, which was somewhat based on the relational model for databases.
Hope you go through about the difference between relational and non relational DB
SQL standard and implementations
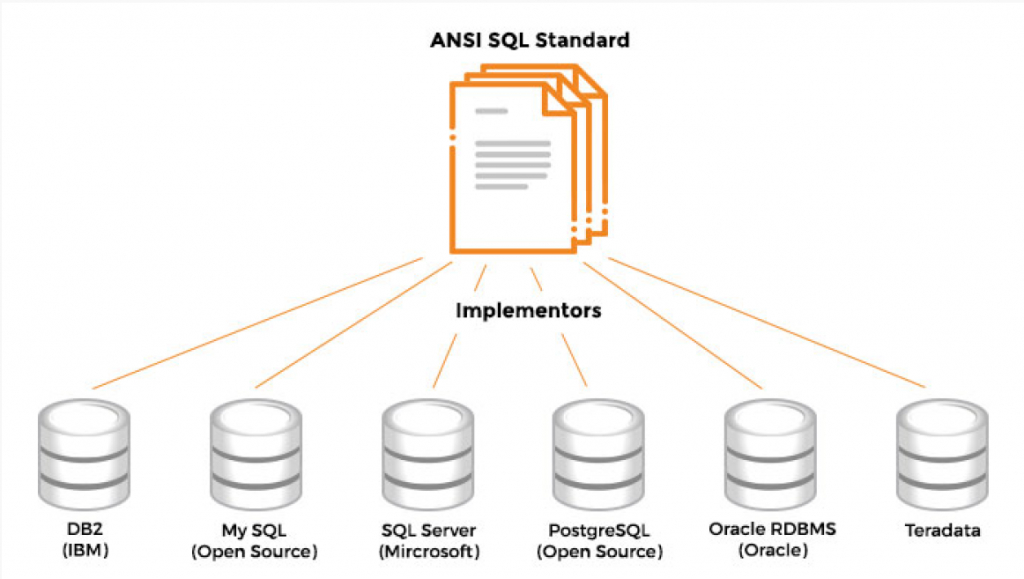
SQL was accepted as a standard by ANSI in 1986 and ISO in 1987. It has been revised a number of times. Various companies have created implementations of this standard. The standard can be thought of as the blueprint that describes the behavior while the actual implementation consists of MySQL, SQL Server, PostgreSQL, etc. The implementations by various vendors are similar because they all conform to the same standard. There are some differences in syntax though. Popular implementations include Oracle RDBMS, IBM DB2, Microsoft SQL Server, Teradata, and MySQL.
SQL is important because many companies have databases based on the relational model that is powered by SQL related technologies.
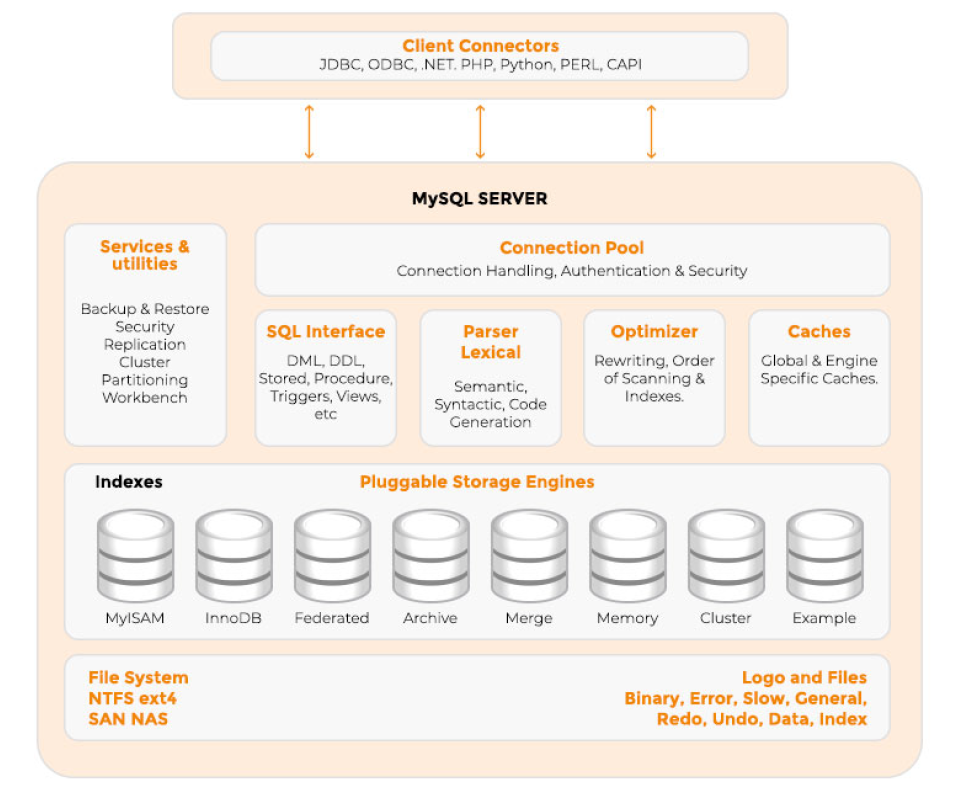
MySQL consists of different components that we’ll discuss in this lesson. MySQL is based on a client-server architecture. Applications such as a website or the MySQL command line client connect and interact with the databases through the MySQL server and the server responds to queries from clients. There are three layers that we can divide MySQL into:
- Application/Client Layer
- MySQL Server Layer
- Storage Engine Layer
Application/Client Layer
The application layer is responsible for client connections, authorization, authentication, and security.
MySQL Server Layer
The server layer is responsible for parsing, analyzing, and optimizing submitted queries. Additionally, it also maintains caches and buffers. MySQL provides other built-in functionality such as recovery and backup partitioning that are also handled by this layer. Lastly, the SQL interface for interacting with the database is also part of this layer. This layer is also referred to as the relational engine. The output of this layer is a query execution plan that is fed into the storage engine. The storage engine then modifies or retrieves data as per the plan.
Storage Engine Layer
The storage engine is that part of the DBMS that actually writes and retrieves data from the underlying physical storage medium. In the case of MySQL, the architecture allows the user to choose the storage engine from a given set of possibilities. Different storage engines are tailored to the needs of the specific use-cases they address. For instance, the InnoDB storage engine supports foreign key constraints and transactions whereas MyISAM is much simpler, lacking those two features but better suited for single-user applications.
[…] Hope you gone through the pervious post […]